The 4 C's
Selecting the right diamond is like building a house. It needs to be the perfect fit for you. Size, color, quality, design, and (most importantly) price are all aspects you need to consider. For diamonds, these descriptions are most commonly referred to as: The Four C's, though we have added cost as a significant aspect making it The 5 C's.
Carat
The weight is the first listed because the initial decision you will want to make is "How Big?" At Scotsman Jewelers you will find a wide variety of diamonds in various weights and sizes: the choice is yours.
Diamonds and other gemstones are measured in carats. Be sure not to confuse Carat with Karat, which is used to identify gold purity. A carat is divided into 100 points. Some may identify a diamond that is under a carat by referencing the amount of points the diamond has. For example, a 40-point diamond weighs 0.40 carats.
It is important to keep in mind that diamonds are not measured by size. Two diamonds that have the same carat weight could look very different in size because a diamond is three-dimensional meaning you have to take into consideration length, width and depth.
Color
The color or lack of color is what helps give a diamond its overall appeal. When professional graders determine the color of a diamond they assign an alphabetical grade to it starting with the letter "D" for diamonds that are colorless and ending with 'Z" for yellow diamonds. Traditionally, diamonds with the least amount of color are considered the most precious.
Clarity
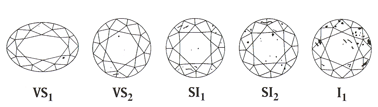
The clarity, or quality, of a diamond can significantly affect the diamonds overall appearance to the naked eye. The less impairments, or inclusions, the better the diamond will appear. The clarity is an evaluation of the diamonds external and internal characteristics. Inclusions are internal: they occur underneath the diamonds surface. When a diamond is evaluated, a professional looks at the size, location, nature, number, and color of all the inclusions and blemishes inside a diamond. This is how a clarity grade is then given to the diamond. Scotsman Jewelers will show you how to properly examine and determine a diamond's clarity, thus ensuring that you receive the best value.
Cut
Cut refers to the shape of a diamond and also the relative proportions of its facets. Round, Marquis, Heart, Princess, Oval, Pear and Cushion are some of the most popular shapes. Even more important than shape, is the diamond's proportions. When a diamond is proportioned properly you get maximum light dispersion and sparkle. It takes a master diamond cutter to reveal a diamond's true beauty. A well-cut diamond reflects light from one mirror-like facet to another and projects the light through the top of the stone. The result is a fiery and brilliant display. Diamonds that are cut too deep or too shallow tend to leak light through the side or bottom which results in a lackluster appearance and also diminished value. At Scotsman Jewelers, you will be able to choose from a variety of diamond shapes so that your perfect match can be found.
The World's Foremost Authority in Gemology
Learn more about diamonds and GIA Diamond Grading Reports
Learn why a GIA Diamond Grading Report is so important
Learn about diamonds from GIA, the creators of the 4Cs and the International Diamond Grading System™
Learn why we carry diamonds graded by GIA
The Definition of Diamond
Exotic and rare, diamonds are perhaps the most treasured gemstone on Earth. Known as the "King of Gems," a diamond glitters and dazzles with its exquisite beauty. But what exactly is diamond, and why is it so special?
Diamonds are … pure, transparent carbon. Carbon—the element fundamental to all life on Earth—is found in its purest, most concentrated form in the mineral diamond. No other form of carbon, and indeed no other mineral on Earth, is as hard or transparent as diamond.
Diamonds are … the hardest natural substance known. The key to a diamond's strength is in its crystal structure. A diamond's carbon atoms link to one another in a rigid, box-like shape, forming the strongest known chemical bond. It's this bond that gives diamond its hardness—its ability to resist scratching. The only substance that can scratch a diamond is another diamond.
Diamonds are … the most brilliant colorless stone. A diamond's intense brilliance is due to its density (the amount of atoms packed into it), which slows light and reflects it back towards the viewer. Diamonds reflect light better than any other colorless substance.
Diamonds are … fiery. A diamond's density also gives it "fire"—the ability to reflect light in a dazzling rainbow of colors. As white light slows down and bounces around inside the dense diamond, it scatters into a fiery spectrum. Diamonds disperse light like a prism better than almost all coloress stones.


colorless: D,E,F,G,H | near colorless: I,J | faint yellow:K,L,M | very light to fancy yellow: N,Z